Bronchitis occurs when the bronchial tubes—airways that carry air in and out of the lungs—become inflamed and produce excess mucus. According to NewYork-Presbyterian (2024), this inflammation often results in persistent coughing, mucus production, and breathing discomfort. Cleveland Clinic (2024) further notes that swollen, mucus-filled airways make it harder to move air effectively, leading to common bronchitis symptoms.
Bronchitis comes in two main forms: acute and chronic, and their causes determine whether they are contagious.
What Is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis refers to irritation and swelling of the bronchial tubes. NewYork-Presbyterian (2024) emphasizes that bronchitis affects the airways, whereas pneumonia affects deeper lung structures called alveoli. Cleveland Clinic (2024) confirms that pneumonia involves inflammation and fluid accumulation in the air sacs, making it generally more serious.
Types of Bronchitis
Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is a short-term illness. According to NewYork-Presbyterian (2024), symptoms usually last two to three weeks, while WebMD (2024) reports a typical duration of one to three weeks. Often, acute bronchitis develops following a cold or flu.
Most cases are caused by viruses, as noted by both NewYork-Presbyterian (2024) and Cleveland Clinic (2024). Cleveland Clinic also documents that certain bacteria—such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae or Bordetella pertussis—may occasionally cause acute bronchitis.
This is the form of bronchitis that can be contagious.
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition defined by a productive cough lasting several months per year for multiple consecutive years. WebMD (2024) and Cleveland Clinic (2024) both confirm this clinical definition.
Chronic bronchitis is primarily linked to long-term irritation, especially tobacco smoke and air pollutants. NewYork-Presbyterian (2024) and Harvard Health (2024) state clearly that chronic bronchitis is not contagious, because it is not caused by an active infection.
Is Bronchitis Contagious?
Whether bronchitis is contagious depends entirely on its cause.
Acute Bronchitis
According to NewYork-Presbyterian (2024), acute bronchitis can be contagious for a few days up to a week. WebMD (2024) emphasizes that the viruses causing acute bronchitis spread easily between people, especially early in the illness when cold-like symptoms are present. Cleveland Clinic (2024) explains that bronchitis itself is not contagious, but the viruses or bacteria that trigger it are.
Chronic Bronchitis
Harvard Health (2024) confirms that chronic bronchitis is not contagious because it stems from long-term airway irritation rather than infection.
How Long Is Acute Bronchitis Contagious?
Bacterial Bronchitis
Cleveland Clinic (2024) reports that if acute bronchitis is bacterial, people may stop being contagious about 24 hours after starting the correct antibiotic.
After One Week
WebMD (2024) notes that individuals may still spread germs if they have fever or frequent coughing, even if a week has passed.
How Bronchitis Spreads
Respiratory infections that cause bronchitis spread in several ways:
- Droplets from coughing, sneezing, or talking (WebMD, 2024)
- Touching contaminated surfaces and then the eyes, nose, or mouth (WebMD, 2024)
Cold weather or getting chilled does not directly cause infectious bronchitis; viruses and bacteria do. This point is supported by CDC guidance stating that bronchitis results from infection rather than cold exposure.
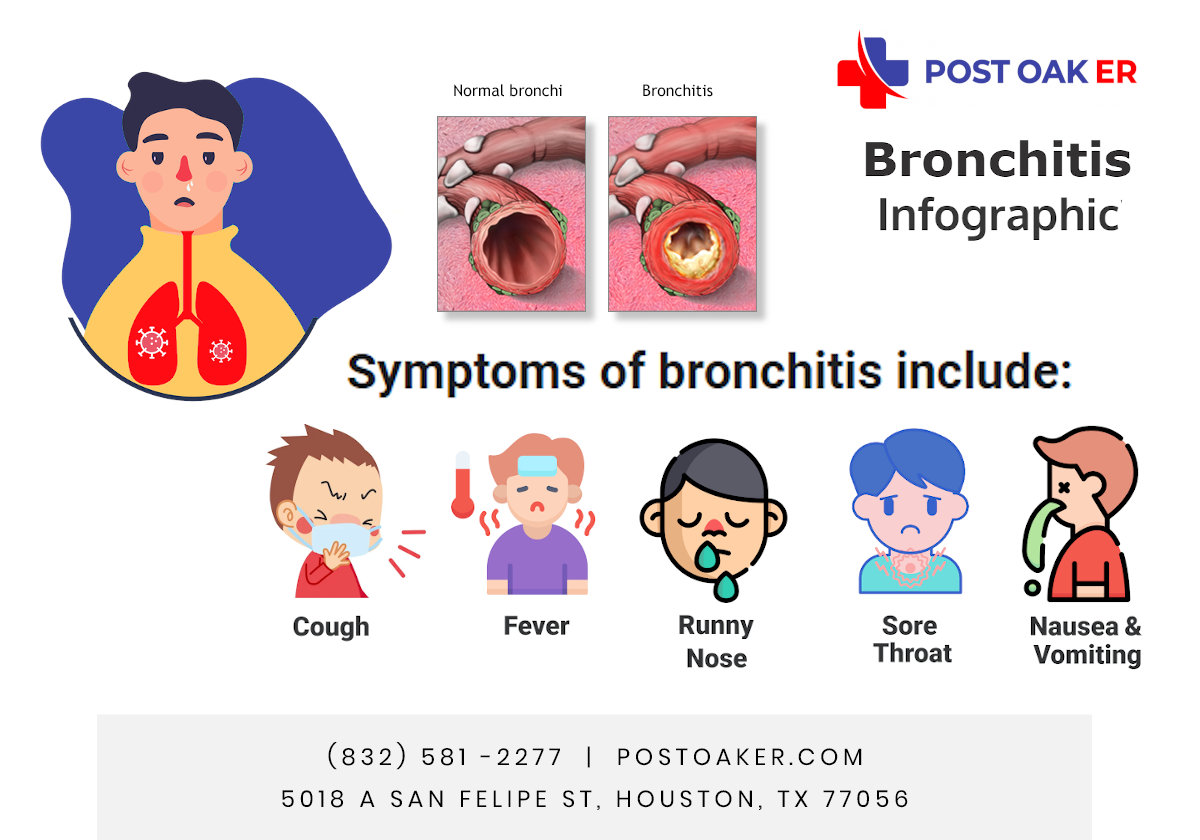
Symptoms of Bronchitis
According to NewYork-Presbyterian (2024), WebMD (2024), and Cleveland Clinic (2024), common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough (with mucus that may be clear, white, yellow, or green)
- Wheezing or shortness of breath
- Chest discomfort or tightness
- Mild fever or fatigue
Warning Signs Requiring Medical Evaluation
WebMD (2024) advises seeking prompt care for:
- Fever above 100.4°F
- Chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Coughing up blood
General emergency medicine guidelines (CDC/AHA) also note that blue lips/face, severe difficulty breathing, fainting, or confusion require immediate emergency attention.
Causes of Bronchitis
Acute Causes
Cleveland Clinic (2024) lists common viral causes including influenza, RSV, adenovirus, and coronaviruses (including COVID-19). Harvard Health (2024) confirms these same viral triggers.
Bacterial causes are less common but include Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Bordetella pertussis (Cleveland Clinic, 2024).
Chronic Causes
NewYork-Presbyterian (2024) identifies:
- Smoking (primary cause)
- Long-term exposure to air pollution or chemical fumes
- Recurrent respiratory infections
Harvard Health (2024) notes chronic bronchitis is often associated with COPD.
Risk Factors
According to NewYork-Presbyterian (2024), Cleveland Clinic (2024), and WebMD (2024), risk factors include:
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Living or working in polluted or dusty environments
- Asthma, COPD, or a history of lung disease
- GERD (NYP, 2024)
- Weakened immune system or chronic health conditions (Cleveland Clinic, 2024)
How Bronchitis Is Diagnosed
Cleveland Clinic (2024) explains that diagnosis typically includes:
- Reviewing symptoms and medical history
- Listening to the lungs for wheezing or crackling
- Checking oxygen saturation
- Testing for viruses (influenza, COVID-19) when appropriate
- Ordering a chest X-ray if pneumonia must be ruled out
Treatment for Bronchitis
Acute Bronchitis
Cleveland Clinic (2024) and Harvard Health (2024) recommend:
- Rest and hydration
- Over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Inhalers or bronchodilators if wheezing
- Humidifiers or warm showers to loosen mucus
Because acute bronchitis is usually viral, Cleveland Clinic (2024) stresses that antibiotics are rarely appropriate.
Chronic Bronchitis
Management focuses on reducing airway irritation and treating underlying lung disease:
- Quit smoking and avoid irritants (NYP, 2024)
- Long-term inhalers (Cleveland Clinic, 2024)
- Pulmonary rehabilitation when COPD is present
- Regular monitoring for flare-ups
At-Home Care Tips
Cleveland Clinic (2024) supports the use of humidifiers, warm liquids, and avoidance of smoke or strong fumes.
Honey may help soothe cough in adults; however, the CDC warns that honey should not be given to children under one year due to the risk of botulism.
Prevention & Reducing Spread
Based on WebMD (2024), Harvard Health (2024), and CDC guidance:
- Wash hands frequently
- Cover coughs and sneezes
- Stay home while symptomatic
- Avoid smoke and pollutants
- Keep distance from others during early, contagious periods
- Stay updated on vaccinations (flu, COVID-19), which reduce infections that can lead to bronchitis
- Cleveland Clinic (2024) additionally recommends pneumonia vaccination for at-risk adults
When to See a Doctor
- WebMD (2024): See a doctor if a cough does not improve after 10 days.
- Cleveland Clinic (2024): See a doctor if symptoms last more than three weeks.
Seek medical care sooner for:
- Persistent or worsening fever
- Worsening shortness of breath or wheezing
- Underlying lung or heart conditions
Pregnant individuals should contact a clinician for any significant respiratory illness due to increased medical risk.
Seek Emergency Care If:
- You experience severe difficulty breathing
- Chest pain resembles heart-related pain (WebMD, 2024)
- Lips or face turn blue or pale
- You faint, become confused, or cannot stay awake (general emergency guidelines)
Frequently Asked Questions
How contagious is bronchitis?
NewYork-Presbyterian (2024), WebMD (2024), and Cleveland Clinic (2024) agree that acute bronchitis is contagious when caused by infection, while chronic bronchitis is not.
How long am I contagious with bronchitis?
Most people are contagious for a few days up to a week (NYP, 2024; Cleveland Clinic, 2024).
WebMD (2024) notes contagiousness may continue as long as cold symptoms persist.
Can bronchitis turn into pneumonia?
WebMD (2024) reports that while bronchitis seldom turns into pneumonia, the risk increases in older adults, smokers, or people with weakened immune systems. Cleveland Clinic (2024) states that pneumonia and bronchitis may share an infection source, but bronchitis does not usually progress into pneumonia.
What’s the difference between bronchitis and pneumonia?
Bronchitis affects the airways; pneumonia affects the air sacs (NYP, 2024; Cleveland Clinic, 2024). Pneumonia is generally more severe.
APA Reference List
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024). Chest cold (acute bronchitis) basics. https://www.cdc.gov/acute-bronchitis/about/index.html
Cleveland Clinic. (2024). Bronchitis: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/3993-bronchitis
Harvard Health Publishing. (2024). Bronchitis. Harvard Medical School.
NewYork-Presbyterian. (2024). Bronchitis overview. https://www.nyp.org
WebMD. (2024). Is bronchitis contagious? https://www.webmd.com/lung/is-bronchitis-contagious
WebMD. (2024). Bronchitis (acute and chronic) basics. https://www.webmd.com/lung/understanding-bronchitis-basics
Mayo Clinic. (2024). Acute bronchitis: FAQ. https://www.mayoclinic.org
American Heart Association. (2024). Emergency warning signs guidance. https://www.heart.org