Key Points at a Glance
- Allergic reaction rashes occur when the immune system reacts to a substance it identifies as harmful.
- Skin findings can include itchy rashes, hives, and swelling; reactions may involve more than one body area.
- Severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) are life-threatening and require immediate emergency care.
- Avoiding known allergens and following clinician guidance are central to management.
- Some commonly asked questions lack high-quality medical evidence; those limits are stated clearly below.
Introduction
An allergic reaction rash is a skin change that occurs when the immune system reacts to a substance it identifies as harmful. Allergic reactions range from mild and localized to severe and life-threatening. Understanding what is well-supported by medical evidence—and what is not—can help you respond appropriately and seek care when needed.
What Is an Allergic Reaction Rash?
Allergic reactions occur when the immune system overreacts to a substance (an allergen). This immune response can trigger the release of inflammatory chemicals that lead to symptoms affecting the skin and, in some cases, other parts of the body. Allergic reactions may be mild or may progress to anaphylaxis, a medical emergency.
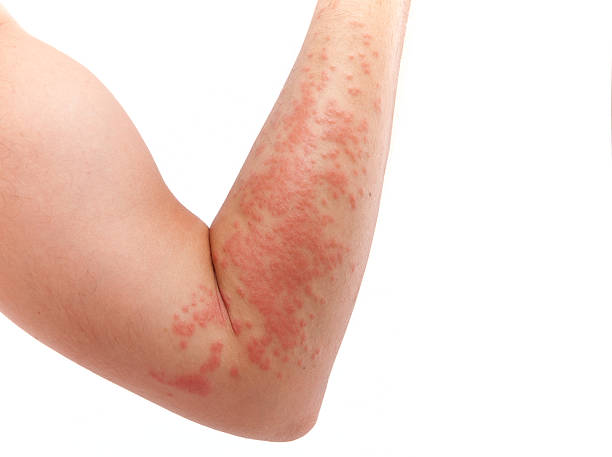
What Does an Allergic Rash Look Like?
Based on verified medical sources, allergic skin reactions may include:
- Red or itchy rash
- Raised, itchy bumps (hives/urticaria)
- Skin swelling
Allergic reactions can affect more than one area of the body at the same time, particularly in more severe reactions.
Evidence gap:
There is no high-quality evidence confirming that allergic rashes reliably appear as pink patches, blistered areas, or that they consistently “move around” the body.
Symptoms: Mild vs. Severe
Mild Allergic Symptoms
Verified mild features include:
- Itchy or slightly swollen skin
- Changes in skin color, such as redness
- Hives
Mild reactions are typically limited but still require monitoring.
Evidence gap:
There is no high-quality evidence confirming that mild allergic reactions affect only the skin or that they consistently resolve with “basic care” alone.
Severe Allergic Symptoms (Possible Anaphylaxis)
Severe allergic reactions may involve multiple body systems and can include:
- Trouble breathing
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, face, or throat
- Dizziness or fainting
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Loss of consciousness in severe cases
Anaphylaxis is life-threatening and requires immediate medical treatment.
Common Causes of Allergic Skin Reactions
Verified causes include:
- Foods
- Medications
- Insect stings
- Latex and other contact exposures
Food allergies can cause skin symptoms such as hives and may also involve the digestive or respiratory systems. In sensitive individuals, very small amounts of a trigger food can cause a reaction.
Medications and insect stings are among the most common causes of severe allergic reactions.
Evidence gap:
There is no high-quality evidence confirming complete lists of contact allergens (such as specific metals or cosmetic ingredients) or that all contact rashes appear exactly where exposure occurred.
What To Do During an Allergic Reaction
If Symptoms Are Mild
- Avoid the known allergen when possible.
- Monitor symptoms closely.
Some medical sources support the use of oral antihistamines for mild allergic symptoms when advised by a healthcare professional.
Evidence gap:
There is no high-quality evidence confirming that washing the skin, cool compresses, or avoiding scratching reliably improves allergic rashes.
If Symptoms Are Severe
- Use epinephrine immediately if it has been prescribed.
- Call emergency services (911) or go to the nearest emergency department.
- Emergency care is required even if symptoms briefly improve.
How Long Do Allergic Reactions Last?
The duration of allergic reactions varies:
- Symptoms may begin within minutes or hours to days after exposure.
- Reactions generally continue as long as exposure to the allergen persists.
- Once exposure stops, symptoms may resolve within hours, though some reactions (such as certain plant-related rashes) can last longer.
Evidence gap:
There is no high-quality evidence confirming specific timelines for hives or drug-related rashes in all cases.
How Clinicians Diagnose Allergic Rashes
Diagnosis may include:
- A medical history and review of exposures
- Physical examination
- Skin testing
- Blood tests
- Patch testing for suspected contact reactions
Testing helps identify triggers and guide management.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the severity and type of allergic reaction and may include:
- Avoidance of known allergens
- Medications, as recommended by a healthcare professional
- Emergency treatment with epinephrine for severe reactions
People with a history of severe allergic reactions are commonly advised to carry epinephrine at all times.
Evidence gap:
There is no high-quality evidence confirming standardized “home remedies” or over-the-counter topical treatments for allergic rashes beyond clinician-guided care.
When to See a Doctor or Seek Emergency Care
Get Emergency Care Immediately If You Have:
- Trouble breathing
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Dizziness, fainting, or loss of consciousness
- Signs of anaphylaxis
See a Doctor Promptly If:
- Allergic symptoms are ongoing or concerning
- You need evaluation to identify possible triggers
- You may require testing or a long-term management plan
Frequently Asked Questions
How are allergic reaction rashes treated?
Treatment depends on severity and cause. Mild reactions may involve avoidance and clinician-advised medications. Severe reactions require immediate emergency care.
Can allergic rashes be life-threatening?
Yes. Some allergic reactions progress to anaphylaxis, which is life-threatening.
How long does an allergic reaction last?
Reactions can last from hours to longer periods depending on exposure and the type of allergen.
What should I do if symptoms suddenly worsen?
Use epinephrine if prescribed and seek emergency care immediately.
What does an allergic reaction rash look like?
Verified evidence shows allergic rashes can appear as itchy, red rashes, hives, or swelling. Other appearances lack high-quality evidence.
How do I get rid of an allergic reaction rash?
Avoiding the allergen and following medical guidance can help.
There is no high-quality evidence supporting this for additional methods.
What can I put on an allergic rash?
There is no high-quality evidence supporting this beyond treatments recommended by a healthcare professional.
How do I calm an allergic reaction on my skin?
Avoid the allergen and seek medical advice.
There is no high-quality evidence supporting this for additional approaches.
APA Reference List
American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. (2025, April 22). Allergic reactions. https://www.aaaai.org/tools-for-the-public/conditions-library/allergies/allergic-reactions
American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. (2025, May 21). Anaphylaxis. https://www.aaaai.org/tools-for-the-public/conditions-library/allergies/anaphylaxis
American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. (2018, February 1). Epinephrine auto-injector. https://acaai.org/allergies/management-treatment/epinephrine-auto-injector/
American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. (n.d.). Drug allergies: Reactions, symptoms & treatment. https://acaai.org/allergies/allergic-conditions/drug-allergies/
Cleveland Clinic. (2025, April 1). Allergies: Types, symptoms, treatment & management. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8610-allergies
Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Contact dermatitis: Symptoms, causes, types & treatments. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/6173-contact-dermatitis
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2023, October 27). Hives and angioedema: Symptoms and causes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hives-and-angioedema/symptoms-causes/syc-20354908
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2024, May 2). Contact dermatitis: Symptoms and causes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/contact-dermatitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20352742
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2024, November 9). Drug allergy: Symptoms and causes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/drug-allergy/symptoms-causes/syc-20371835
Mayo Clinic Staff. (n.d.). Anaphylaxis: First aid. https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-anaphylaxis/basics/art-20056608
National Library of Medicine. (2024, March 31). Allergic reactions (Medical Encyclopedia). MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000005.htm
National Library of Medicine. (2024, March 31). Anaphylaxis (Medical Encyclopedia). MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000844.htm
National Library of Medicine. (2024, March 31). Drug allergies (Medical Encyclopedia). MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000819.htm
National Library of Medicine. (2025, April 1). Hives (Medical Encyclopedia). MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000845.htm
National Library of Medicine. (2025, August 2). Contact dermatitis (Medical Encyclopedia). MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000869.htm